Episode Frequency And Duration
Next, we investigated whether the decline in shedding rates over time was attributable to reduced frequency or shorter duration of episodes. The mean frequency of episodes over a 1-year period for the entire cohort was 14.4 episodes of total HSV-2 shedding, 11.6 episodes of subclinical shedding, and 8.7 episodes with genital lesions. Episode frequency did not change significantly over time since first herpes episode.
The duration of clinical recurrences decreased after the first year following the first genital HSV-2 episode. The mean recurrence length was 10.4 days among participants < 1 year from their first herpes episode, 7.2 days among those 19 years , and 6.5 days among those 10 years from first herpes episode . These decreases remained significant among those 19 years , and those 10 years from first herpes episode after adjusting for race. In contrast to clinical recurrences, the duration of total and subclinical episodes did not change significantly by year since initial HSV-2 episode. The mean duration of any viral shedding episode was 4.6 days, and mean subclinical episode length was 2.6 days for the entire cohort.
What Happens If Herpes Is Not Treated
Herpes can be painful, but it generally does not cause serious health problems like other STDs can.
Without treatment, you might continue to have regular outbreaks, or they could only happen rarely. Some people naturally stop getting outbreaks after a while. Herpes typically does not get worse over time.
The information on this page is adapted from the CDC and Planned Parenthood.
Who Might Get Herpes Simplex
People of any age can contract herpes simplex. You are more likely to get the virus if you:
- Were assigned female at birth.
- Have had multiple sex partners.
- Started having sex at a young age.
- Have a history of any sexually transmitted infection .
- Have a weakened immune system.
- Dont use condoms for intercourse and dental dams for oral sex.
Who gets HSV-1, commonly known as oral herpes?
Anyone can get HSV-1. Most people contract HSV-1 during childhood. It spreads when an adult who has the virus has close contact with a child, such as when a family member kisses a child.
Who gets HSV-2, commonly known as genital herpes?
Genital herpes affects sexually active teens and adults of all genders and races. It can spread if you have multiple sexual partners and dont use condoms or dental dams.
People assigned female at birth are more at risk. Delicate vaginal tissue can tear, making it easier for the infection to get in. Black people who were AFAB are especially vulnerable, with an estimated 1 in 2 people AFAB between the ages of 14 and 49 infected with HSV-2.
Read Also: How Does Herpes Get Tested
What Is Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections . The infection can be bothersome.
Most people never have symptoms, or the symptoms are so mild that people don’t know that they are infected. But in some people, the infection causes occasional outbreaks of itchy and painful sores in the genital area.
After the first outbreak, the herpes virus stays in the nerve cells below the skin and becomes inactive. It usually becomes active again from time to time, travelling back up to the skin and causing more sores. Things like stress, illness, a new sex partner, or menstruation may trigger a new outbreak. As time goes on, the outbreaks happen less often, heal faster, and don’t hurt as much.
What Are Herpes Recurrences And How Likely Are They

Recurrences are repeat symptoms which appear at or close to the place where the infection was first noticed. These are often fairly minor and may be no more than a small spot that heals in a few days. They may be accompanied by sensations itches or nerve twinges. They are unlikely to be as severe as first symptoms and may be almost unnoticed.
Read Also: Will Abreva Work On Genital Herpes
How Does Genital Herpes Spread
Herpes can be spread when an infected person has lesions blisters and open sores on their body or when you do not have any symptoms. Taking antiviral medicine can help you reduce the risk of spreading genital herpes to your sexual partners. You can also:
- Inform your sexual partner that you have genital herpes.
- Use a condom every time you have sex.
- Refrain from having sex when you have symptoms.
- Abstain from performing oral sex if you have blisters or open sores around your mouth.
Complications Of Cold Sores
Cold sores are usually mild, but may cause complications in rare cases. People with weak immune systems caused by illness or treatments such as chemotherapy are particularly at risk of complications.
Dehydration sometimes occurs if drinking fluids becomes painful. Young children are particularly at risk of becoming dehydrated.
The herpes simplex virus can also spread to other parts of your body. Examples of when this can occur include:
- skin infections these often occur if the virus comes into contact with broken skin, such as a cut or graze, or a skin condition such as eczema
- herpetic whitlow this causes painful sores and blisters to appear on and around your fingers
- herpetic keratoconjunctivitis this causes swelling and irritation of your eye area and sores to develop on your eyelids
Left untreated, herpetic keratoconjunctivitis can cause the cornea, the transparent layer at the front of your eye, to become infected, which can eventually lead to blindness.
Itâs therefore important not to touch your eyes if you have an unhealed cold sore. If you must touch your eyes for example, to remove contact lenses wash your hands thoroughly first.
In very rare cases, encephalitis, a condition where the brain becomes inflamed and swollen, can be caused by the cold sore virus spreading to the brain. It can be treated with intravenous injections of antiviral medications, such as aciclovir.
Medically reviewed by Michele Emery, DNP
Read Also: How Long Does Herpes Take To Clear Up
Condoms And Antiviral Meds Can Reduce Transmission Risk
Herpes is transmitted through contact with skin and oral or genital mucosa, and lesions do not have to be visible for the virus to be transmitted. Using a condom can decrease the risk of spreading or acquiring genital herpesbut it’s not 100% effective, said Dr. Swartz, because the virus can be on parts of the genital area that are still exposed.
For people who know they have an infection, taking daily antiviral medication can also cut the odds of spreading HSV to partners. Common antiviral medications include Sitavig and Zovirax , Valtrex , and Famvir . In fact, because of ulcers and nerve damage that can be caused by HSV infection, antiviral therapy is recommended for anyone experiencing a first episode of genital herpes, according to the CDC.
More Questions From Patients:
Many people with genital herpes have no symptoms, or have very mild symptoms that go unnoticed.
The first time genital herpes symptoms appear is called the “first episode” or “initial herpes.” Initial herpes symptoms are usually more noticeable than later outbreaks.
Symptoms of genital herpes in men may include
-
burning when you pee if you have sores
-
trouble peeing if you have sores covering your urethra
-
itching or pain around your genitals
During initial herpes, symptoms may also include
-
swollen, tender glands in the pelvic area, throat, or under the arms
Don’t Miss: How To Not Catch Genital Herpes
What Increases Your Risk
Things that increase your risk of getting genital herpes include:
- Having more than one sex partner.
- Having a high-risk partner or partners .
- Having unprotected sexual contact .
- Starting sexual activity at a young age. The younger people are when they start having sex, the greater their risk is of getting genital herpes.
- Having a weakened immune system.
- Being a woman. Women are more likely than men to become infected when exposed to genital herpes. And their symptoms tend to be more severe and longer-lasting. Women also are at a greater risk of having complications from a genital herpes infection.
Having herpes, especially if you have open sores, also increases your risk for becoming infected with HIV if you are exposed to HIV.
Any child with genital herpes needs to be evaluated by a doctor to see if it is the result of sexual abuse. For more information, see the topic Child Abuse and Neglect.
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Labialis
Recurrent herpes simplex labialis, also known as oral herpes, is a condition of the mouth area caused by the herpes simplex virus. Its a common and contagious condition that spreads easily.
According to the World Health Organization , an estimated two out of three adults in the world under age 50 carry this virus.
The condition causes blisters and sores on the lips, mouth, tongue, or gums. After an initial outbreak, the virus stays dormant inside the nerve cells of the face.
Later on in life, the virus can reactivate and result in more sores. These are commonly known as cold sores or fever blisters.
Recurrent herpes simplex labialis usually isnt serious, but relapses are common. Many people choose to treat the recurrent episodes with over-the-counter creams.
The symptoms will usually go away without treatment in a few weeks. A doctor may prescribe medications if relapses occur often.
Read Also: How Long After Outbreak Is Herpes Contagious
What Does Genital Herpes Look Like
While some people with genital herpes will never have any symptoms, other people can develop symptoms within a few weeks of being infected.
Often, before the lesions appear, patients describe a prodrome, characterized by a tingling or burning sensation in the area where the lesions will develop that can be noticed during urination, along with itching or discomfort in the genital area.
You can also have the following symptoms:
- Blisters on the mouth or lips
- Fever, headache or pain in the joints
- Trouble urinating
The symptoms of genital herpes often go away and come back as recurring outbreaks. For most people, the first outbreak is the worst, and can last from two to three weeks. Future flare-ups are often less severe and do not last as long. Still, some people shed the virus regularly. The following triggers can make outbreaks more likely to occur:
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Menstrual periods
Recurrent genital herpes is most common in the first year after the initial infection and decreases as time goes on.
In many cases, anti-herpes medicine can help patients. When a person experiences a prodrome and suspects a recurrence is going to happen, they begin taking anti-herpes medications that lessen symptoms and shorten the time of the outbreak.
Ruling Out Conditions That Resemble Oral Herpes
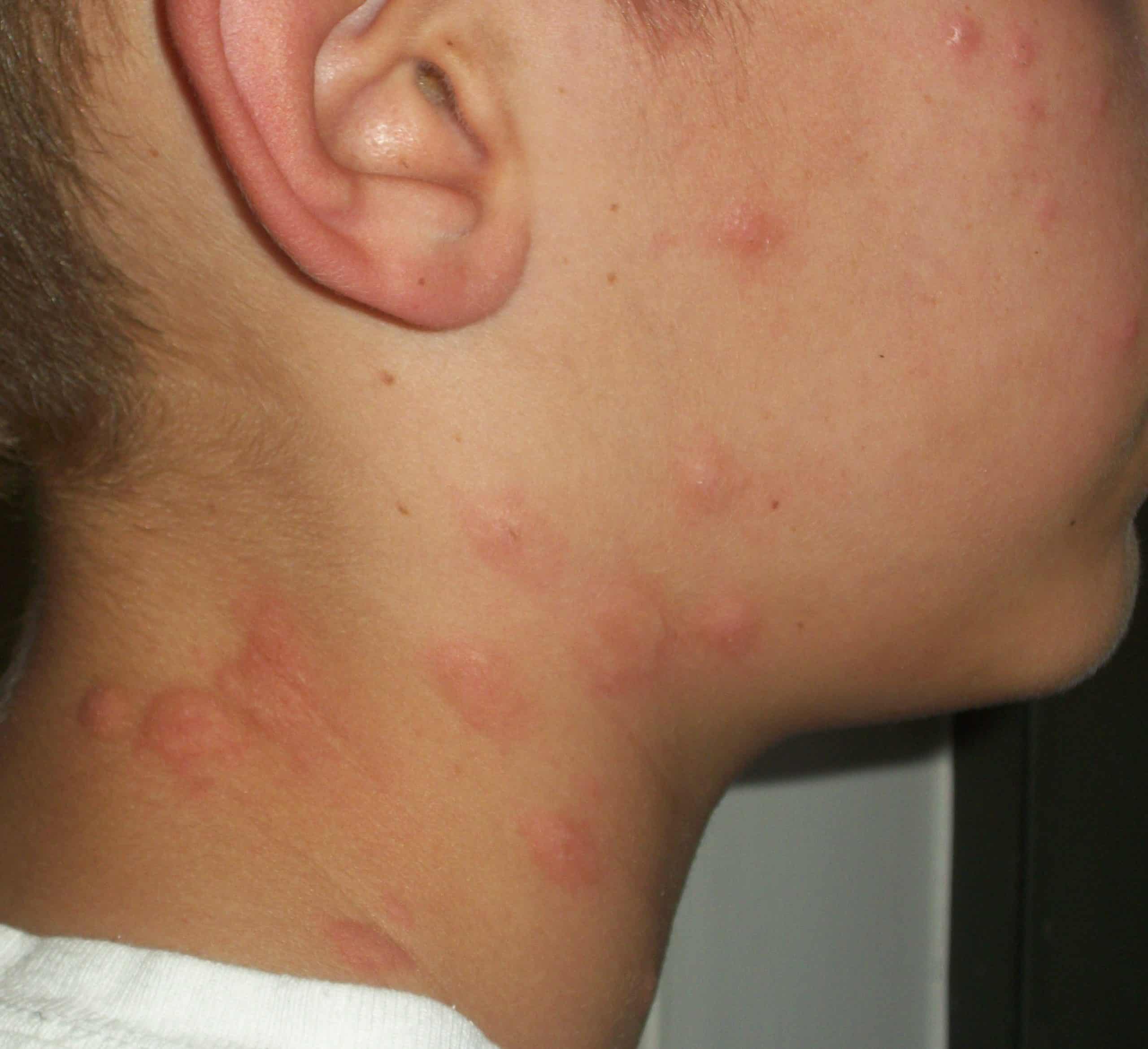
Canker Sores
Simple canker sores are often confused with the cold sores of HSV-1. Canker sores frequently crop up singly or in groups on the inside of the mouth, or on or underneath the tongue. Their cause is unknown, and they are common in perfectly healthy people. They are usually white or grayish crater-like ulcers with a sharp edge and a red rim. They usually heal within 2 weeks without treatment.
This aphthous ulcer is located in front of and just below the bottom teeth.
Thrush
Oral candidiasis is a yeast infection that causes a whitish overgrowth in the mouth. It is most common in infants, but can appear in people of all ages, particularly people taking antibiotics or those with impaired immune systems.
Other conditions that may be confused with oral herpes include herpangina , sore throat caused by strep or other bacteria, and infectious mononucleosis.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Herpes Flare Ups
How Often Can Genital Herpes Come Back
Some people get no further episodes, while a few get frequent recurrences. If you do, you could ask your doctor for antiviral pills to prevent outbreaks see antiviral treatment, or you can try self-help treatments. There are two pages of suggestions on our Tips to prevent recurrences leaflet. It is available to members. Outbreaks normally decline in frequency and severity over time.
Warning Signs Of An Outbreak
Before a full outbreak occurs, many people go through prodromal herpes symptoms, or the signs that an outbreak is about to start.
- One may feel abdominal pressure, general aches and pains in the muscles, burning, tingling, or itching sensations and general tenderness around the infected area.
- More acute symptoms cause pain in the groin or inner thighs, painful urination, and unusual or heavy vaginal discharge.
These various symptoms will often be preceded by more common, flu-like symptoms of infection. Swollen lymph nodes, fever, chills, fatigue, nausea and a general body ache could mean youve contracted something more than the flu.
If you get these prodrome signs, take extra care to avoid HSV recurrence triggers. And avoid sex until they are completely gone so you dont pass HSV to your partner.
Also Check: How To Prevent Genital Herpes Transmission
Lets Stop Making Hsv2 Into Such A Big Deal
For whatever reason, herpes is among the most feared STIs despite the fact that other common STIs are high risk for complications. While herpes, on the other hand, might cause little to no symptoms at all. There are two probable reasons for this:
#1. A lacking sexual education system leaves us in the dark when it comes to common sexually transmitted infections and diseases. So, left to our own devices, we get our sexual education from movies and the greater mass media- which can skew reality and induce shame for no reason.
#2. The fear might also stem from the fact that herpes is a lifelong virus. But there are proven and easily accessible ways to reduce outbreaks and have a sex life that is both enjoyable and low partner-to-partner transmission risk. Some people with herpes have little to no outbreaks and keep their reoccurrences under control with the help of antiviral medications.
Treatments Your Physician May Prescribe
Most HSV infections are easy for physicians to diagnose. On occasion, however, a swab from the infected skin may be sent to the laboratory to confirm the diagnosis. A blood test may also be performed to determine if you have been exposed to the virus. Your doctor may also recommend a blood test for your partner to determine if he/she has been exposed to herpes in the past, or is at risk for contracting the virus.Untreated HSV infections will go away on their own, but antiviral medications can reduce symptoms, shorten the duration of outbreaks, and decrease the chance of spreading the virus. These medicines are most effective if taken during the first 24 hours of symptoms. If you experience burning and tingling before the appearance of blisters, you can start the medicine as soon as you feel these symptoms. Unfortunately, these medicines do not cure HSV infections.Treatment for primary and recurrent HSV infections are oral antiviral medications, such as acyclovir , valacyclovir , and famciclovir . Each of these medications is equally effective and usually taken for 710 days for primary infections and 15 days for recurrent infections. Talk to your doctor about getting a prescription for these medicines for possible future outbreaks, as they are most effective if taken early on.More severe HSV infections may require additional medications such as:
Recommended Reading: How To Suppress Herpes Virus
Embed This Infographic On Your Site
< span data-mce-type=bookmark style=display: inline-block width: 0px overflow: hidden line-height: 0 class=mce_SELRES_start> < /span> < /p> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < p> < strong> Please include attribution to justherpes.com with this graphic.< /strong> < /p> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < p> < a href=https://justherpes.com/facts/herpes-outbreak-triggers/> < img src=https://justherpes.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/herpes-outbreak-triggers-infographic.jpg alt=HSV Outbreak Triggers Infographic 540px border=0 /> < /a> < /p> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < br /> < p>
Colds Fever And Immunity Busters
Getting another illness like the common cold can bring on herpes outbreaks because your immune system is busy fighting the new thing.
A fever is popularly known to cause HSV-1 outbreaks, or cold sores, giving them the name fever blisters.
Those with compromised or taxed immune systems will have more frequent herpes outbreaks. After all, thats the reason things like UV light, which affects immunity, and fighting off other illnesses are outbreak triggers at all.
An immune system compromised by receiving chemotherapy can lead to more outbreaks, as can an immune system weakened by HIV.
Read Also: How To Treat Herpes Sores On Buttocks
How Do You Treat Herpes
Theres no cure for herpes, but prescription medications can ease symptoms, end outbreaks sooner, and lower the chances of passing the virus to other people.
You can also help ease the pain caused by herpes outbreaks by taking a warm bath, wearing loose clothing and putting an ice pack on the sores.
What Are The Herpes Outbreak Stages

- Lauren Stuttaford
Herpes, otherwise known as the herpes simplex virus, is categorized into two types: herpes simplex virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2 .
The first is mainly transmitted through oral-to-oral contact causing oral herpes but can also cause genital herpes. While HSV-2 is a sexually transmitted infection that causes genital herpes. Both types of the infection are lifelong.
A person infected with herpes, whether oral or genital, might show no symptoms or could progress through the different herpes outbreak stages from blister development to herps healing. However, most herpes infections are asymptomatic.
According to the World Health Organization , an estimated 3.7 billion people under 50 years old have HSV-1 infection globally, and an estimated 491 million people between the ages of 15-49 have HSV-2 infection worldwide.
Astonishingly, the virus causing genital herpes or HSV-2 increases the risk of contracting and transmitting HIV, putting millions at greater risk of contracting an HIV infection.
Lets take a closer look at the herpes outbreak stages.
Read Also: Do Antibiotics Help Herpes Outbreak