Herpes May Raise Cervical Cancer Risk Study Finds
Herpes simplex-2, the virus that causes genital herpes, may act as an accomplice to another virus known to cause cervical cancer, making a woman even more susceptible to cancer, according to a new report. The researchers reported their findings in the article “Herpes Simplex Virus-2 as a Human Papillomavirus Cofactor in the Etiology of Invasive Cervical Cancer” in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute .
Human papillomavirus is the major cause of cervical cancer, which killed an estimated 4,400 women in the United States last year. Scientists have long suspected that other STDs could add to the risk. HSV-2 was a prime suspect, but studies had not come to any clear conclusion.
Jennifer Smith of the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon, France, and colleagues around the world looked at specimens from more than 1,200 cervical cancer patients in several countries and compared them to samples from 1,100 other women of similar ages and circumstances. They analyzed their blood for evidence of HSV-2, HSV-1 , and chlamydia. They found 44 percent of the women with cancer had genital herpes as opposed to 25 percent of women without cancer. “HSV-2 infection may act in conjunction with HPV infection to increase the risk of invasive cervical carcinoma,” they wrote.
Different Ways Of Using Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 For The Treatment Of Human Cancers
Broadly speaking, there are two types of HSV-1 vectors, both have been used in cancer treatment. Replication-defective vectors, in which transgene expression cassettes are inserted in a viral genome with one or a few essential viral genes deleted. Such vectors can effectively express transgene products, but are unable to replicate, except in cells that complement the deleted viral functions in trans. A special group of replication-defective HSV vectors are amplicons., , , In this approach, an expression cassette for the therapeutic transgene is placed in a plasmid that contains the viral packaging/cleavage signals and HSV-1 origin of replication. Defective HSV-like particles that contain concatemerized plasmid DNA is produced in eukaryotic cells that supply viral functions in trans. Conditionally replicating vectors, in which deletion of some nonessential viral genes results in viruses that preferentially infect, replicate in, and lyse tumor cells. Conditionally replicating vectors can also be modified to carry therapeutic transgenes to augment antitumor effects. This review focuses on the recent progress in using replication-defective and conditionally replicating HSV-1 vectors for the treatment of human cancers.
Recommended Reading: How To Kill Herpes On Surfaces
C History Part : Competing Diagnoses That Can Mimic Herpes Viruses
Not too many diseases cause the dermatomal distribution that is seen with herpes virus infections.
Differential diagnosis for HSV-1 and oral lesions includes recurrent aphthous ulcers, aphthous stomatitis, syphilis, bacterial pharyngitis, Epstein-Barr virus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, contact dermatitis, bullous impetigo, and enteroviruses.
The differential for genital ulcers includes syphilis, chancroid, drug eruptions, contact dermatitis, molluscum contagiosum, lymphogranuloma venerum, and Behcets disease.
Read Also: Are You Born With Herpes
Why Is Hpv Vaccination Important
The combination of HPV vaccination and cervical screening can provide the greatest protection against cervical cancer. Also, HPV vaccination reduces the risk of developing cancers caused by HPV at sites other than the cervix.
Not only does vaccination protect vaccinated individuals against infection by the HPV types targeted by the vaccine that is used , but vaccination can also reduce the prevalence of the vaccine-targeted HPV types in the population, thereby reducing infection in individuals who are not vaccinated . For example, in Australia, where a high proportion of girls are vaccinated with Gardasil, the incidence of genital warts went down during the first 4 years of the vaccination program among young maleswho were not being vaccinated at the timeas well as among young females .
Further evidence that large-scale HPV vaccination confers protection for unvaccinated individuals comes from a 2019 meta-analysis of girls-only HPV vaccination programs in 14 high-income countries that included 60 million vaccinated people . That analysis showed that, up to 8 years after the start of vaccination, diagnoses of anogenital warts decreased by 31% among women aged 2529 years, by 48% among boys aged 1519 years, and by 32% among men aged 2024 years, compared with the period before vaccination began.
How Do Hpv Vaccines Work
Like other immunizations that guard against viral infection, HPV vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies that, in future encounters with HPV, bind to the virus and prevent it from infecting cells.
The current HPV vaccines are based on virus-like particles that are formed by HPV surface components. VLPs are not infectious because they lack the viruss DNA. However, they closely resemble the natural virus, and antibodies against the VLPs also have activity against the natural virus. The VLPs have been found to be strongly immunogenic, which means that they induce high levels of antibody production by the body. This makes the vaccines highly effective.
The vaccines do not prevent other sexually transmitted diseases, nor do they treat existing HPV infections or HPV-caused disease.
Read Also: How To Relieve Herpes Pain
Risk Factors For Cervical Cancer
Many women have probably heard of cervical cancer but do not think it will affect them. Cervical cancer is more prevalent in mid-life and the American Cancer Society predicts that about 12,900 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in 2015. There are ways to prevent certain kinds of cervical cancer but it is not 100% preventable. Cervical cancer has its own unique set of risk factors and symptoms and they should be watched for. Below we discuss what the most common risk factors and symptoms of cervical cancer are so that you can take the best care of your body.
Risk Factors:
What Imaging Studies Should Be Ordered To Help Establish The Diagnosis How Should The Results Be Interpreted
Magnetic resonance imaging brain should be obtained in patients with suspected HSV encephalitis. In most cases of HSV encephalitis, MRI will reveal edema and/or abnormal enhancement in one or both temporal and frontal lobes, the insular cortex, and the angular gyrus. If MRI cannot be obtained, computed tomography brain is acceptable, but less sensitive.
You May Like: Does Black Seed Oil Cure Herpes
How Much Does Hpv Vaccination Cost And Will Insurance Pay For It
Most private insurance plans cover HPV vaccination. The federal Affordable Care Act requires most private insurance plans to cover recommended preventive services with no copay or deductible.
Medicaid covers HPV vaccination in accordance with ACIP recommendations, and immunizations are a mandatory service under Medicaid for eligible individuals under age 21. In addition, the federal Vaccines for Children Program provides immunization services for children younger than 19 years who are Medicaid eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or Native American or Alaska Native.
Merck, the manufacturer of Gardasil 9, offers the Merck Vaccine Patient Assistance Program, which provides Gardasil 9 for free to people aged 19 to 45 years who live in the United States, do not have health insurance, and have an annual household income less than a certain amount.
How Common Is Hpv And Health Problems That Develop From Hpv
HPV : CDC estimates that there were 43 million HPV infections in 2018. In that same year, there were 13 million new infections. HPV is so common that almost every sexually active person will get HPV at some point if they dont get vaccinated.
Health problems related to HPV include genital warts and cervical cancer.
Genital warts: Prior to HPV vaccines, genital warts caused by HPV affected roughly 340,000 to 360,000 people yearly.* About one in 100 sexually active adults in the U.S. has genital warts at any given time.
Cervical cancer: Every year, nearly 12,000 women living in the U.S. will have cervical cancer. More than 4,000 women die from cervical cancereven with screening and treatment.
There are other conditions and cancers caused by HPV that occur in people living in the United States. Every year, about 19,400 women and 12,100 men experience cancers caused by HPV.
*These figures only look at the number of people who sought care for genital warts. This could be less than the actual number of people who get genital warts.
You May Like: How Is Genital Herpes Transmitted 5 Points
Who Should Get Hpv Vaccination
The Centers for Disease Control and Preventions Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices develops recommendations regarding all vaccination in the United States, including HPV vaccination. The current ACIP recommendations for HPV vaccination are :
- Children and adults ages 9 through 26 years. HPV vaccination is routinely recommended at age 11 or 12 years vaccination can be started at age 9 years. HPV vaccination is recommended for all persons through age 26 years who were not adequately vaccinated earlier.
- Adults ages 27 through 45 years. Although the HPV vaccine is Food and Drug Administration approved to be given through age 45 years, HPV vaccination is not recommended for all adults ages 27 through 45 years. Instead, ACIP recommends that clinicians consider discussing with their patients in this age group who were not adequately vaccinated earlier whether HPV vaccination is right for them. HPV vaccination in this age range provides less benefit because more people have already been exposed to the virus.
- Persons who are pregnant. HPV vaccination should be delayed until after pregnancy, but pregnancy testing is not required before vaccination. There is no evidence that vaccination will affect a pregnancy or harm a fetus.
Oral Herpes And Cold Sores
Cold sores are a symptom of oral herpes .
Cold sores are blister-like sores that occur near the mouth or lips. They can also occur on other areas of the face. They typically persist for 2 weeks or more. Because theres no cure for herpes, cold sores can come back.
Genital herpes is quite common.
Although genital herpes is typically caused by HSV-2, the infection can also be caused by HSV-1.
According to the WHOs latest available statistics, it was estimated that 491.5 million people had an HSV-2 infection in 2016. This is over one-tenth of the worlds population ages 15 to 49 years.
The WHO also estimates that 3.7 billion people had an HSV-1 infection in the same year, which accounts for around two-thirds of the worlds population under age 50 years.
CDC does not recommend getting tested for herpes.
However, if there are symptoms of genital herpes, its important to see a doctor. They can make a diagnosis and discuss management strategies for the infection.
Additionally, if theres a potential of having been exposed to HSV, or if theres a desire to get a full STI exam and testing, its recommended to schedule an appointment with a doctor.
If an in-person appointment is not possible, an at-home test kit is another option to consider. However, its important to note that an in-person test done by a doctor may be more accurate.
Treatment can reduce outbreaks, but it cannot cure herpes simplex viruses.
Don’t Miss: Doctors Who Specialize In Herpes
Is There Treatment For Hpv Or Health Problems That Develop From Hpv
There is no treatment for the virus itself. However, there are treatments for the health problems that HPV can cause:
You can add this content to your website by syndicating.
F Prognosis And Patient Counselling
Counselling is a crucial aspect in the management of herpes. Patients should be counselled that herpes is a chronic, lifelong viral illness that may result in frequent recurrent outbreaks. Over time, patients learn their triggers, such as stress, as well as early prodromal symptoms to initiate immediate therapy. Patients should also be counselled on the appropriateness of chronic suppressive therapy versus episodic treatment for recurrences. Patients with genital herpes should inform their sexual partners of their genital herpes and use latex condoms to help reduce but not eliminate the risk of transmission. Lastly, patients need counselling on the risk of neonatal HSV transmission. Pregnant women should be asked if they have ever had genital herpes. Women with genital herpes lesions present at the time of labor should undergo caesarian delivery to reduce the risk of neonatal HSV.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When You Think You Have Herpes
Breast Cancer Awareness: Even Common Herpes Virus Could Put Women At Risk
Women, beware! Some of the most common viruses, some belonging to the Herpes family, may put you at increased risk for developing breast cancer. One such a virus is called Epstein-Barr virus .
EBV, one of eight known viruses in the herpes family to infect humans, is also known as the cause of infectious mononucleosis and has been linked to various cancers, including African Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkins disease, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma and leiomyosarcoma.
Association of EBV infection with breast cancer has been reported in several studies, but it was unclear how the virus plays a role in breast cancer development or progression.
To reveal the reason, the researchers cultured breast cells called primary mammary epithelial cells in the presence of EBV.
The researchers found that the EBV infection binds to the CD21 receptor on normal breast cells, leading to infection and inducing characteristics of stem cells, which then keeps dividing.
Lytic Infection Vs Latency
In a fraction of neurons harboring latent HSV-1, the virus is periodically reactivated. Cascade expression of the viral IE, E and L genes resumes, resulting in the production of mature virions. Infectious virus particles are transported to the peripheral nerve terminals by anterograde axonal transport pathway, released, and infect cells at or near the site of initial infection. Reactivation is not completely understood, but external stimuli, such as UV light, stress and fever, are known for decades to induce HSV-1 reactivation. Depending on several factors, including the host immune status, the reactivation may be asymptomatic or lead to a recurrent lesion, which may vary considerably in severity from punctuate lesions that are invisible to naked eyes to severe, debilitating lesions in immunocompromised individuals.
You May Like: What Does Herpes Simplex Look Like
Does Ebv Cause Cancer
The Epstein Barr virus increases the risk of some cancer types. But, for most people that have the virus, it will not cause them any problems.
EBV is linked to Hodgkin lymphoma , Burkitt lymphoma and nasopharyngeal cancers.
Its not possible to predict who will develop EBV-linked cancer and who wont. But there are other important things you can do to reduce your risk of cancer, such as not smoking, keeping a healthy weight and cutting down on alcohol.
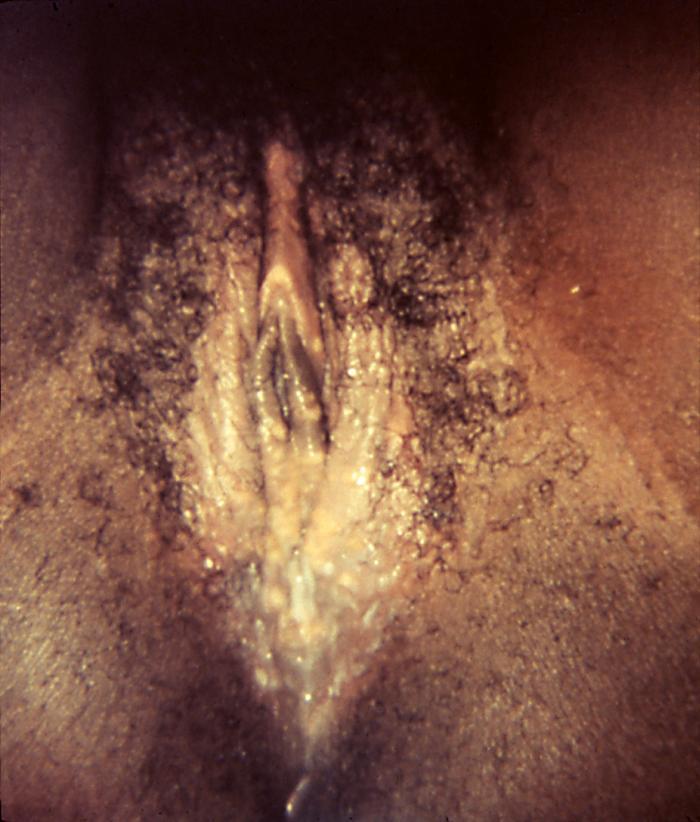
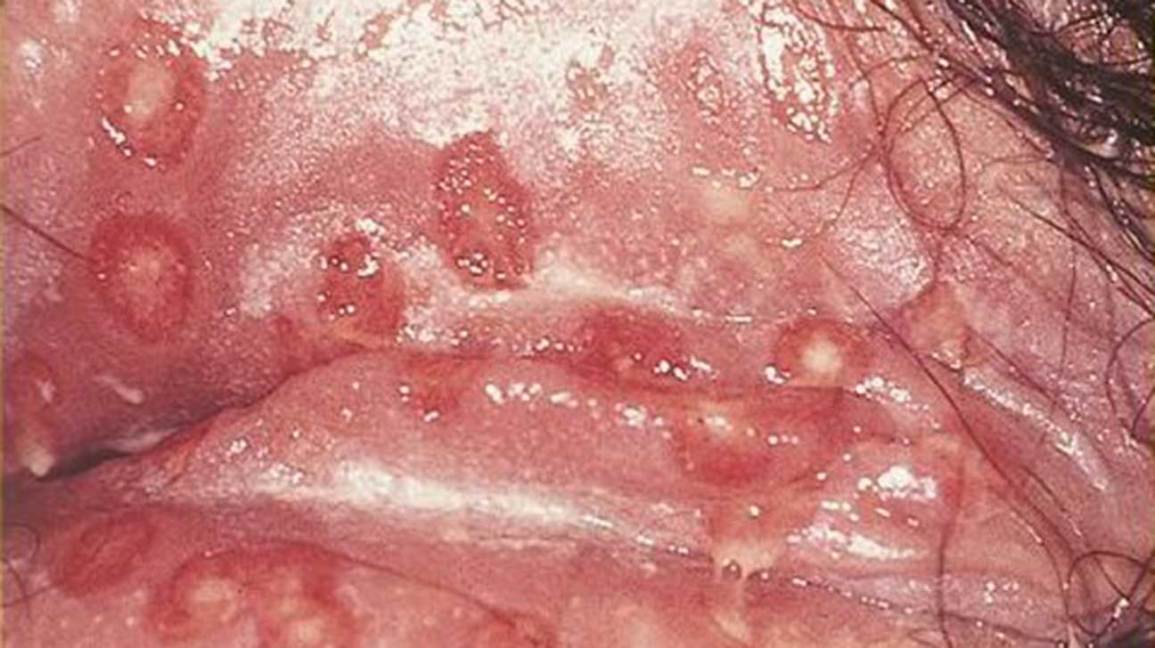
Symptoms Of Genital Herpes
Herpes simplex can produce both symptoms of the outer body or be experienced by the sufferer depending on whether the infection is recurrent or you have it for the first time.
These include:
- Tingling and pain in the genitals
- Rash characteristic of lesions or blisters or ulcers
Individuals who have recurrent episodes experience the symptoms in shorter periods but they are less severe.
Statistically, genital herpes is more common in women than there are male cases.
Also Check: Can You Contract Herpes Without Having Intercourse
What Is Herpes What Is Herpes Zoster
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted disease caused by the herpes simplex virus . It spreads primarily via sexual contact. The virus can lie dormant in your body after the initial infection and can reactivate several times a year.
Genital herpes can cause, pain, itching, and sores in the genital area. There are no signs and symptoms of genital herpes. If you are infected, you can be contagious even if there are no visible sores. Genital herpes has no cure. Medications can lessen the symptoms and reduce the chance of infecting others.
In contrast, herpes zoster is a viral infection that causes an outbreak of a painful rash or blisters on the skin. The same virus that causes chickenpox causes the varicella-zoster virus which causes shingles.
No Ulcers Doesnt Equal No Herpes So Then What
If youve never had genital ulcers and as far as you know, have never been exposed, is it worth getting tested? Thats a controversial point and in fact, the widely followed official guidelines discourage screening.
Why? Many reasons: Lets say the test comes back positive for HSV-2. This means that the patient may have been exposed to HSV-2 at some point in their lives, somehow, somewhere. Research tells us that these folks may be periodically shedding virus particles in their genital fluids. These patients would then be diagnosed with genital herpes, encouraged to share their status with future partners, and offered daily antiviral medication to prevent possibly spreading the virus.
All of this can be a tough pill to swallow, so to speak. There is significant social stigma and shame associated with herpes. In addition, there are occasionally false-positive tests. Labeling someone with the diagnosis can be devastating to their future relationships, and asking someone to take a pill for a condition they may or may not have and may or may not spread seems unreasonable.
However, many experts disagree with the official guidelines. I wrote to Dr. John Gnann, professor of infectious disease at the Medical University of South Carolina and co-author of a review in the New England Journal of Medicine . He has suggested the below guidelines, and outlines the rationale:
You May Like: How To Avoid Spreading Herpes
B Appropriate Prophylaxis And Other Measures To Prevent Readmission
Consideration for chronic suppressive therapy if a patient has severe frequent outbreaks.
2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.. .
Fanfair, RN, Zaidi, A, Taylor, LD, Xu, F, Gottlieb, S, Markowitz, L. Trends in seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus type 2 among non-Hispanic blacks and non-Hispanic whites aged 14 to 49 years United States, 1988 to 2010. Sex Transm Dis. vol. 40. 2013. pp. 860-4.
Kennedy, PG, Rovnak, J, Badani, H, Cohrs, RJ. A comparison of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus latency and reactivation. J Gen Virol. vol. 96. 2015 Jul. pp. 1581-602.
Kennedy, PG, Steiner, I. Recent issues in herpes simplex encephalitis. J Neurovirol. vol. 19. 2013 Aug. pp. 346-50.
Le Cleach, L, Trinquart, L, Do, G. Oral antiviral therapy for prevention of genital herpes outbreaks in immunocompetent and non-pregnant patients. . vol. 8. 2014. pp. CD009036
Levitz, RE. Herpes simplex encephalitis: a review. Heart Lung. vol. 27. 1998. pp. 209
Sawleshwarkar, S, Dwyer, DE. Antivirals for herpes simplex viruses. BMJ.. vol. 351. 2015 Jul 9. pp. h3350
Steiner, I, Schmutzhard, E, Sellner, J, Chaudhuri, A, Kennedy, PG. EFNS-ENS guidelines for the use of PCR technology for the diagnosis of infections of the nervous system. Eur J Neurol. vol. 19. pp. 1278-1291.