Is A Vaccine Available To Prevent Shingles
Two vaccines are available in the United States to reduce your chance of developing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. One vaccine, Zostavax®, has been available since 2006. The second vaccine, Shingrix®, has been available since 2017. Shingrix is recommended as the preferred vaccine by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of medical and public health experts.
Shingrix® is given as a two-dose shot in the upper arm. You should receive the second dose two to six months after receiving the first. Shingrix has been shown to be more than 90% effective in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. Its effectiveness remains above 85% for at least four years after receiving the vaccine.
Due to high levels of demand for the Shingrix vaccine and a supply shortage, the vaccine manufacturer is managing the timing and distribution of the vaccine throughout the United States. It plans to continue to manage the availability of the vaccine and hopes to make available the same or increased number of doses and to shorten the wait time for delivery this year .
What Host Factors Protect Against This Infection
Research has shown that T-cell mediated immunity protects an individual from herpes zoster reactivation later in life. The patients most at risk are the elderly, as they have decreased cell mediated immunity, and immunocompromised individuals. Patients on immunosuppressive medications, including, but not limited, to cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and high dose prednisone are at increased risk.
Why Doesnt Having Chickenpox Earlier In Life Provide Immunity Against Having Shingles Later
After having chickenpox, your body does not rid your system of the virus. Instead, the virus stays in a portion of the spinal nerve root called the dorsal root ganglion. In most people, the virus simply stays there quietly and doesnt cause problems. Scientists arent always sure why the virus gets active again, but they know stress can be a cause.
Recommended Reading: Can Herpes Be Controlled With Medication
What Is The Contagious Period For Shingles
The virus that causes shingles, the varicella-zoster virus, can be transmitted from person to person by direct contact with the fluid from the active blistering rash. Therefore, susceptible individuals should avoid contact with people who have active shingles, especially pregnant women who have never had chickenpox and immunocompromised individuals. It cannot be transmitted by coughing or sneezing, and it is not contagious before the blisters appear. Once the shingles rash has dried and developed crusting, it generally is not considered to be contagious.
There are a few important points to consider when discussing the varicella-zoster virus and transmissibility.
- If an individual who has never had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine comes in direct contact with the fluid from the shingles rash, they may go on to develop chickenpox, but they will not immediately develop shingles.
- It is possible, however, for them to develop shingles later in life, just as it is with others who have previously been exposed to the virus and developed chickenpox.
- Also, if you have previously been exposed to the varicella-zoster virus and you have had chickenpox, you will not contract the virus from others with shingles.
Clinical Aspects Of Hz

The cause of the dermatomal pain becomes obvious when the characteristic rash appears in that dermatome . The interval from the onset of the prodrome to the appearance of rash represents the time required for reactivated VZV to replicate in the ganglion and to transit down the cutaneous nerve to the nerve endings at the dermal-epidermal junction. There is additional delay while VZV replicates in the skin and induces sufficient necrosis and inflammatory response to cause the rash.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
HZ is a dermatomal illness that does not cross the midline except where the normal representation of segmental nerves does so to a limited extent. In immunocompetent patients, only a single dermatome is typically affected however, normal variations in innervation can lead to limited involvement of adjacent dermatomes. In typical HZ, widespread involvement of multiple dermatomes, especially those that are widely separated, does not occur. The rash is usually accompanied by the same pain experienced during the prodrome, but this acute pain can worsen, improve, or appear for the first time during the cutaneous phase of HZ. Pruritis may be as common as pain in patients with HZ, although it has received far less medical attention . Some mild cases of HZ are characterized by more pruritis than pain.
Disseminated herpes zoster
Don’t Miss: How To Heal Herpes Outbreak
What Can Be Done For Recurrent Shingles
Though most people will experience only one episode of shingles during their lifetime, recurrence can occur in certain individuals. In order to help prevent recurrent episodes of shingles, individuals with no contraindications can receive the zoster vaccine , which can prevent recurrent episodes of shingles. Otherwise, people who do experience a recurrent case of shingles should see their doctor as soon as the rash appears to promptly receive antiviral medication.
What Are The Risks Associated With Shingles
Some people experience pain around the rash site for a month or morepain that is severe enough to interfere with daily activities.
Scratching the rash can also cause a secondary infection if harmful bacteria get into the sores.
Shingles on the face can involve the eyes, which is serious because it can cause scarring and blindness.
The occurrence and severity of shingles and its complications increase with age.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Getting Genital Herpes
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Shingles
Shingles can often be diagnosed by your doctor based upon the distinctive appearance and distribution of the characteristic shingles rash. A painful, blistering rash that is localized to defined dermatomes is a sign highly suggestive of shingles. Blood work or other testing is usually not necessary. Diagnosing shingles before the appearance of the rash or in cases of zoster sine herpete can be challenging. In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, laboratory tests are available to help confirm the diagnosis. Depending on the clinical situation, testing can be done using either blood work or by specialized testing of skin lesion samples.
How Common Is Herpes Meningitis
Because herpes meningitis often resolves on its own, not all cases are recorded, so it’s unclear exactly how common it is. For some perspective, older data show that tens of thousands of meningitis-related hospitalizations in the United States are due to a virus like a herpes virus. Experts believe most cases of herpes meningitis are caused by HSV-2, which is present in roughly 12% of U.S. adults under age 50.
Read Also: How To Make Herpes On Lip Go Away Faster
What Are The Symptoms
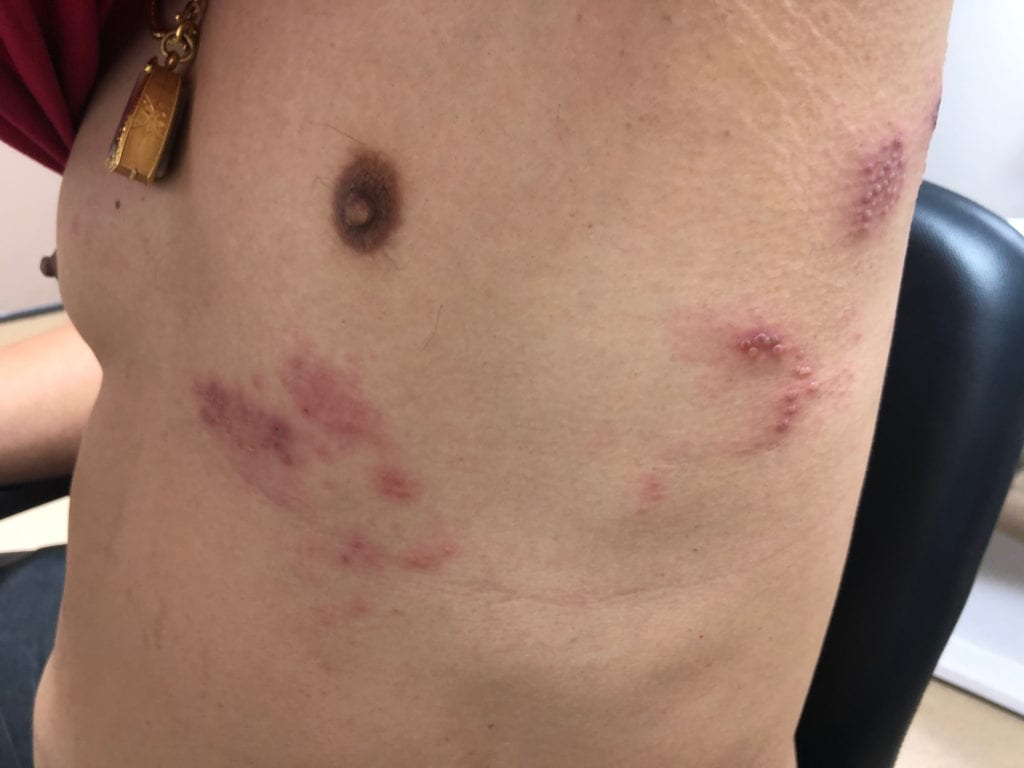
The first sign of shingles is often burning, sharp pain, tingling, or numbness in your skin on one side of your body or face. The most common site is the back or upper abdomen. You may have severe itching or aching. You also may feel tired and ill with fever, chills, headache, and upset stomach or belly pain.
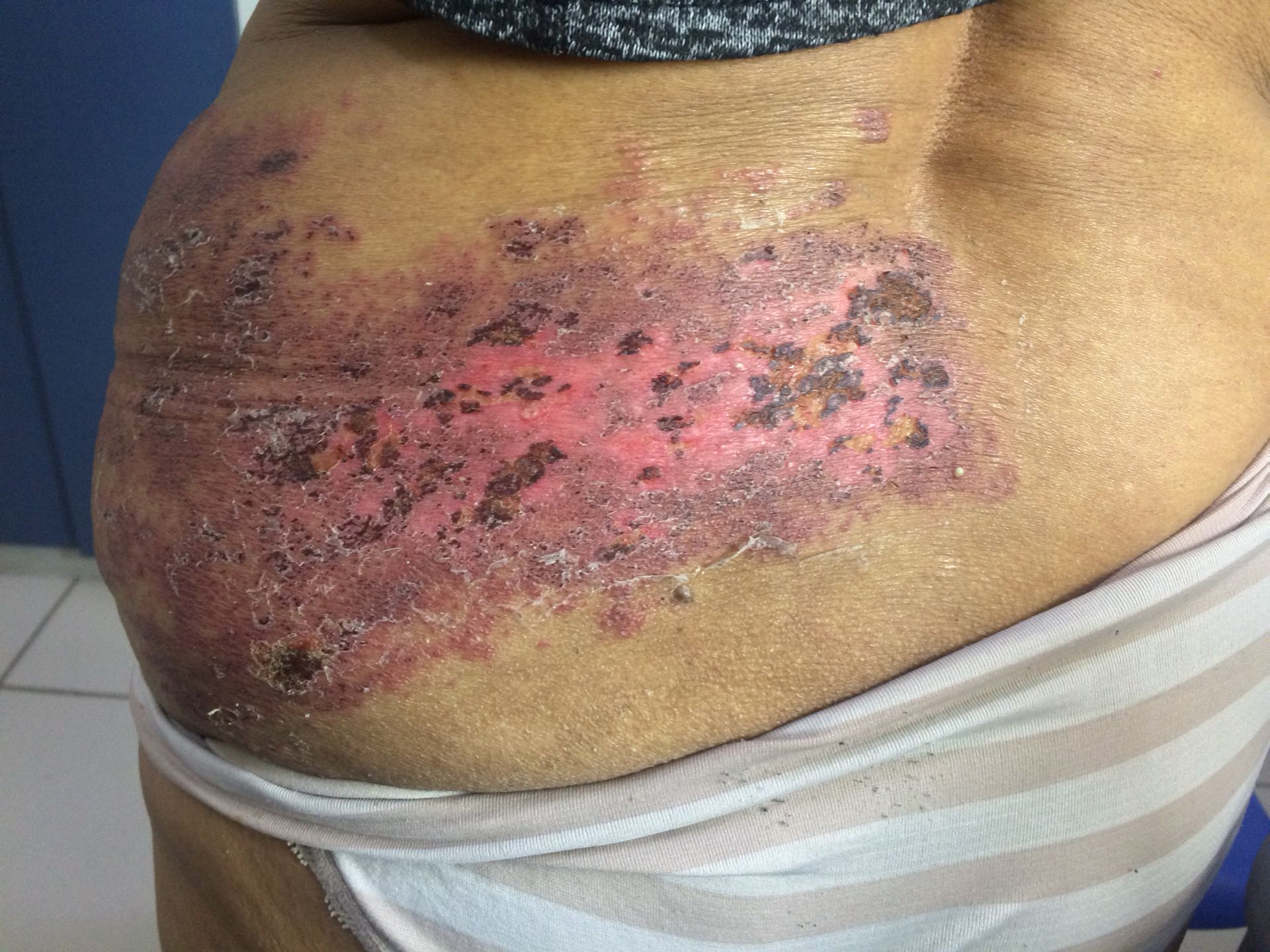
One to 14 days after you start feeling pain, you will notice a rash of small blisters on reddened skin. Within a few days after they appear, the blisters will turn yellow, then dry and crust over. Over the next 2 weeks the crusts drop off, and the skin continues to heal over the next several days to weeks.
Because shingles usually follows nerve paths, the blisters are usually found in a line, often extending from the back or side around to the belly. The blisters are almost always on just one side of the body. Shingles usually doesn’t cross the midline of the body. The rash also may appear on one side of your face or scalp. The painful rash may be in the area of your ear or eye. When shingles occurs on the head or scalp, symptoms can include headaches and weakness of one side of the face, which causes that side of the face to look droopy. The symptoms usually go away eventually, but it may take many months.
In some cases the pain can last for weeks, months, or years, long after the rash heals. This is called postherpetic neuralgia.
How Should I Identify The Organism
There are multiple detection methods for herpes virus. For the most part, diagnosis of herpes zoster is based on clinical symptoms and distribution of dermatomal rash exhibited by the patient. Diagnostic testing may be performed on fluid from the vesicles or from cerebrospinal fluid. A polymerase chain reaction test, which has the greatest specificity and sensitivity, confirms the presence of VZV DNA. PCR testing is preferred in almost all situations. The direct immunofluorescent antibody test has a lower sensitivity and specificity of 70-76%. Finally, the viral culture, which was previously used, has a low sensitivity of 20% and takes longer to process, and as such it is rarely used.
Read Also: How To Boost Immune System To Fight Herpes
Treatment Of Immunocompetent Patients
The principal goals of the treatment of HZ are reduction of pain in immunocompetent patients and cessation of viral replication in immunocompromised patients and those with ophthalmic HZ. All patients should have a medical and psychosocial history evaluation and targeted physical examination performed to confirm the diagnosis, document comorbid illnesses, and provide a basis for treatment. Prompt referral to an ophthalmologist is required for all patients with ocular involvement, whether immunocompetent or immunocompromised. Elderly patients may be socially isolated, have cognitive impairment or depression, or have had recent adverse major life events , all of which may impact treatment compliance and response to treatment. Anxiety or depression may also develop secondary to severe HZ, which may further complicate treatment and disease resolution.
Comparison With Existing Literature
Studies from the US, Italy, and Australia report higher proportions of patients with herpes zoster receiving antiviral prescriptions. A retrospective study of healthcare records in Italy between 2003 and 2005 found 78% of 3260 immunocompetent patients with herpes zoster aged 50 years received antivirals.15 In Australia analysis of healthcare records between 20002006 showed that 73.5% of 379 incident zoster cases aged 50 years received antivirals16 and a similarly high proportion was found in the US where 71.3% of 8741 newly diagnosed zoster adults received antivirals 17 both studies included immunosuppressed and immunocompetent individuals. In contrast, data from a large database of general practice records in the Netherlands in 2001 found 22.5% of 1129 patients with herpes zoster aged 44 years received antivirals.18 Observed variation in prescribing patterns between countries may reflect differences in healthcare systems or distribution of patients with characteristics more/less likely to get antivirals in study populations, or to variations in data quality.
Also Check: Has Anyone Gotten Rid Of Herpes
How Does This Organism Cause Disease
Younger patients are either infected with varicella virus, causing chickenpox, or vaccinated with the live varicella vaccine. The virus then remains dormant in individuals as long as cell mediated immunity is intact.
VZV remains dormant in the dorsal root ganglion, and zoster occurs once the virus reactivates. The virus then travels down the cell axon to the sensory terminals located near the skin. The rash is created once the virus invades the skin and causes an inflammatory response.
Prevention And Treatment Of Postherpetic Neuralgia
A systematic review6 considered 42 RCTs of therapies to prevent or reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia pain. Acyclovir reduced the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia pain at three months .
Famciclovir reduced the duration of postherpetic neuralgia pain better than placebo.3 The time to resolution of pain in patients 50 years of age or older was significantly shorter for two dosages of famciclovir than for placebo .
Systemic steroids have demonstrated no additional benefit. Studies examining amitriptyline, narcotics, capsaicin, anticonvulsants, and percutaneous nerve stimulation for postherpetic neuralgia were of fair to poor quality and no conclusions could be drawn from these.
Read Also: Is It Safe To Have Sex With Herpes
Can I Get Shingles If I Havent Had Chickenpox
No. You cant get shingles if youve never had chickenpox, but you can get chickenpox from someone who has shingles. If youve never had chickenpox and you come into direct contact with the oozing, blister-like rash of someone with shingles, the varicella-zoster virus can infect you and you would develop chickenpox.
Once youve had chickenpox, you could develop shingles at some point in your life. This is because the varicella-zoster virus never fully goes away after youve had chickenpox. It lies quietly inactive in your nerve tissue. Later in life, the virus may become active again and appears as shingles.
Is Herpes Meningitis Contagious
Herpes meningitis by itself is not contagious, but the viruses that cause it are.
The viruses that cause herpes meningitis are transmitted through close contact with another person or their bodily fluids, such as saliva, urine, blood, genital fluids, or breast milk.
For example, a person who is infected with a virus that causes herpes meningitis can transfer it to another person by:
- Coughing or sneezing
- Sharing personal products, like a razor or toothbrush
- Contact with contaminated surfaces
Keep in mind that just because you’ve contracted one of the common herpes viruses doesn’t automatically mean you will develop herpes meningitis as a complication. Older research found that 36% of women and 13% of men with HSV-2 reported developing herpes meningitis.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Herpes On Chin
Is The Zostavax Vaccine Still Being Used
Yes. It is still recommended for preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia in healthy people age 50 and older. Zostavax is given as a single-dose shot versus the two-dose shot for Shingrix. Zostavax is less effective than Shingrix in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia .
Zostavax can be considered if you are allergic to Shingrix or if Shingrix is unavailable due to supply shortage and you want some immediate protection from a possible case of shingles and/or postherpetic neuralgia. Because it is a weakened live vaccine, it may be dangerous if you have cancer, HIV, or take steroids, chemotherapy or other medications that suppress your immune system. Ask your healthcare provider if the Zostavax vaccine is an option for you.
What Are The Topical Treatment Options For Herpes Zoster
There are a variety of topic treatments, including topical acyclovir 5% cream, lidocaine, and capsaicin. The latter, applied at least 5 times a day, depletes neurotransmitters at involved nerve endings. Topical lidocaine can also be used to treat patients with PHN. For acute HZO, a good approach is wet-to-dry dressings with sterile saline solution or Burow solution , which should be applied to the affected skin for 30-60 minutes 4-6 times daily. A modified form of Burow solution is commercially sold as Domeboro powder packets, which need to be dissolved in water. The acyclovir cream is often applied 5 times a day for 4 days. Calamine lotion, a mixture of zinc oxide with about 0.5% iron oxide, may be used as an antipruritic agent. It is also used as a mild antiseptic to prevent infections that can be caused by scratching the affected area, as well as an astringent for weeping or oozing blisters. There is, however, no proof that calamine lotion has any real therapeutic effect on rashes and itching. Topical ozone therapy may be beneficial in diminishing pain and shortening the course, with few if any adverse effects.
References
Dworkin RH, Johnson RW, Breuer J, Gnann JW, et al. Recommendations for the management of herpes zoster. Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jan 1. 44 Suppl 1:S1-26. .
Goh CL, Khoo L. A retrospective study of the clinical presentation and outcome of herpes zoster in a tertiary dermatology outpatient referral clinic. Int J Dermatol. 1997 Sep. 36:667-72. .
Also Check: How To Make Herpes Go Away Faster
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Anyone experiencing symptoms of a potential herpes meningitis infectionsuch as a constant headache, unexplained fever, and neck painshould contact a healthcare provider or seek medical care as soon as possible. This is particularly important for babies and people with weakened immune systems.
While forms of viral meningitis like herpes meningitis are not usually life-threatening, they can potentially become serious if not properly diagnosed and treated early.
What Causes Herpes Meningitis
Herpes meningitis is a viral meningitis, which means that the meningitis is caused by a virus.
A person may develop herpes meningitis if theyve contracted a herpes virus, including:
- Epstein-Barr virus , a common virus that causes mononucleosis and other illnesses
The viruses that cause herpes meningitis enter the body through your skin, where they can travel through the central nervous system and potentially cause problems in other parts of the body, like the tissues surrounding the CNS.
Once a herpes virus is in your system, it’s possible to get herpes meningitis at any time. That’s because the virus stays in your body for life and goes through periods of inactivity and flare-ups .
Recommended Reading: Which Doctor To Consult For Herpes
Treatment Of Common Cutaneous Herpes Simplex Virus Infections
DAVID H. EMMERT, M.D., Lancaster General Hospital, Lancaster, Pennsylvania
Am Fam Physician. 2000 Mar 15 61:1697-1704.
Herpes simplex virus infection is increasingly common in the United States. New antiviral medications have expanded treatment options for the two most common cutaneous manifestations, orolabial and genital herpes. Acyclovir therapy remains an effective and often less expensive option. Famciclovir and valacyclovir offer improved oral bioavailability and convenient oral dosing schedules but are more expensive than acyclovir. Patients who have six or more recurrences of genital herpes per year can be treated with one of the following regimens: acyclovir, 400 mg twice daily valacyclovir, 1 g daily or famciclovir, 250 mg twice daily. These regimens are effective in suppressing 70 to 80 percent of symptomatic recurrences. Episodic treatment of recurrent genital herpes is of questionable benefit, but it may be helpful in appropriately selected patients. There is little evidence indicating benefit from treatment of recurrent orolabial herpes, which tends to be mild and infrequent.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Oral Herpes