How Is Shingles Treated
There is no cure for shingles but there are treatments for managing the symptoms. Antiviral medications may ease the discomfort and reduce the duration of the symptoms, particularly if started within 72 hours of the first sign of shingles. Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen can be effective in relieving mild pain. Antibacterial agents can be given to treat bacterial infections of the shingles rash .
How Can I Prevent Herpes Zoster
The CDC recommends vaccination at age 50-60 for all individuals who have had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine. Zostavax® is a single dose live virus vaccine recommended starting at age 60. Shingrix® is a newer non-live vaccine given in two doses starting at age 50. Shingrix has been found to be more than 90% effective in preventing shingling and PHN. Zostavax is less effective 50% effective in preventing shingles, 67% effective in preventing PHN.
Can Other People Catch It
This one is confusing! You can catch chickenpox from other people, but you can’t catch shingles from other people. You only get shingles from a reactivation of your own chickenpox infection in the past.
So if you have shingles, and you come into contact with somebody else, they cannot ‘catch’ your shingles. But if they have never had chickenpox, it is possible that they could catch chickenpox from you.
To put it another way, no, you don’t ‘catch’ shingles. It comes from a virus hiding out in your own body, not from someone else. But if you have shingles, you may be infectious, as it is possible for people to catch chickenpox from you.
Only people who have never had chickenpox are likely to be at risk of catching chickenpox from your shingles. People who have had chickenpox should be immune from catching it again. If the rash is in a covered area of skin, the risk of anyone with whom you are not in close contact catching chickenpox is very low.
You May Like: What Topical Cream Can I Use For Herpes
How Do You Shingles Treatment
Some people have such mild symptoms of shingles that they dont seek medical treatment. At the other extreme, severe symptoms may result in a visit to the emergency room. What you can do. You may want to write a list that includes: A detailed description of your symptoms Information about your medical problems, past and present
Who Is At Risk For Getting Shingles

People who have had chickenpox who are more likely to develop shingles include:
- People with a weakened immune system .
- People over the age of 50.
- People who have been ill.
- People who have experienced trauma.
- People who are under stress.
After having chickenpox, your body does not rid your system of the virus. Instead, the virus stays in a portion of the spinal nerve root called the dorsal root ganglion. For the majority of people, the virus stays there quietly and doesn’t cause problems. We aren’t always sure why the virus gets reactivated, but this typically occurs at times of stress.
Don’t Miss: How To Naturally Get Rid Of Herpes Outbreak
Shingles Rash On Hands
They could then develop shingles later in life. The risk of spreading VZV to others is low if you cover the shingles rash. People with shingles cannot spread the virus before their rash blisters appear or after the rash crusts. People with chickenpox are more likely to spread VZV than people with shingles.
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Shingles
Shingles can often be diagnosed by your doctor based upon the distinctive appearance and distribution of the characteristic shingles rash. A painful, blistering rash that is localized to defined dermatomes is a sign highly suggestive of shingles. Blood work or other testing is usually not necessary. Diagnosing shingles before the appearance of the rash or in cases of zoster sine herpete can be challenging. In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, laboratory tests are available to help confirm the diagnosis. Depending on the clinical situation, testing can be done using either blood work or by specialized testing of skin lesion samples.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Oral Herpes Outbreak Fast
How Is It Treated
It is best to start treatment as soon as possible after you notice the rash. See your healthcare provider to discuss treatment with antiviral medicine, such as acyclovir. This medicine is most effective if you start taking it within the first 3 days of the rash. Antiviral medicine may speed your recovery and lessen the chance that the pain will last for a long time.
Your provider may also recommend or prescribe:
- medicine for pain
- antibacterial salves or lotions to help prevent bacterial infection of the blisters
- corticosteroids
What Is The Treatment For Herpes Zoster
Immediate treatment with antiviral drugs may help lessen the duration and severity of some of the symptoms. These antiviral medications are more effective the sooner they are started. Medications like acetaminophen and ibuprofen may help alleviate some of the pain, but the disease has to run its course. Use of medication will be determined by your primary care provider based on factors including duration and severity of the symptoms.
You May Like: Can You Stop Herpes Before It Starts
What Are The Treatments For Shingles
There is no cure for shingles. Antiviral medicines may help to make the attack shorter and less severe. They may also help prevent PHN. The medicines are most effective if you can take them within 3 days after the rash appears. So if you think you might have shingles, contact your health care provider as soon as possible.
Pain relievers may also help with the pain. A cool washcloth, calamine lotion, and oatmeal baths may help relieve some of the itching.
What Are The Symptoms Of Herpes Zoster
The rash associated with herpes zoster most often occurs on the trunk and buttocks. It may also appear on the arms, legs, or face. While symptoms may vary child to child, the most common include:
- skin hypersensitivity in the area where the herpes zoster is to appear
- mild rash, which appears after five days and first looks like small, red spots that turn into blisters
- blisters, which turn yellow and dry, often leaving small, pitted scars
- rash goes away in one to two weeks
- rash is usually localized to one side of the body
Read Also: How Can You Not Spread Herpes
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
National and international surveillance is performed by the CDC to determine effectiveness of the current FDA-approved antiviral flu drugs. Public health officials use this information to make current recommendations about the use of flu antiviral medications. WHO further recommends in-depth epidemiological investigations to control potential transmission of the resistant virus and prevent future progression. As novel treatments and detection techniques to antiviral resistance are enhanced so can the establishment of strategies to combat the inevitable emergence of antiviral resistance.
Certain Herbs Useful In Herpes Zoster Infection

- Lemon Herb – A cup of herbal tea prepared by adding a few leaves of lemon herb, is found effective in shingles infection.
- Chamomile – It is antiviral herb and chamomile bath can be very beneficial to get relief from the symptoms of shingles infection.
- Mullein – Leaves as well flowers of this herb provide relief from pain caused due to shingle.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Second Herpes Outbreak Last
What Types Of Health Care Professionals Treat Shingles
Shingles is most commonly diagnosed and treated by a primary care physician or an emergency medicine physician. For certain individuals who develop complications of shingles, a specialist in ophthalmology, neurology, or infectious disease may also be involved. Select patients with postherpetic neuralgia may require the care of a pain specialist.
What Are The Complications Of Herpes Zoster
- Involvement of several dermatomes, or sometimes, bilateraleruptions in unique dermatomes
- Eye complications when the ophthalmic division of the fifth cranial nerve is involved
- Deep blisters that take weeks to heal followed by scarring
- Muscle weakness in about one in 20 patients. Facial nerve palsy is the most common result . There is a 50% chance of complete recovery, but some improvement can be expected in nearly all cases
- Infection of internal organs, including the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and brain
Herpes zoster is infectious to people who have not previously had chickenpox.
Herpes zoster in the early months of pregnancy can harm the fetus, but luckily this is rare. Shingles in late pregnancy can cause chickenpox in the fetus or newborn. Herpes zoster may then develop as an infant.
Don’t Miss: Where Is The Cure For Herpes
Is There A Shingles Vaccine
In the UK there is a shingles vaccine immunisation programme for people aged 70 years to protect against herpes zoster. There is also a catch-up programme which offers the vaccine to certain people aged between 70 and 79 years who may have previously missed out on immunisation. The vaccine is licensed for people aged over 50 years, and if you are not eligible for the vaccine on the NHS, your pharmacist may be able to provide the vaccine as a private service.
The chickenpox vaccine is not routinely given to children in the UK but is offered to people who are in close contact with someone who is particularly vulnerable to chickenpox or its complications – eg, people with a weakened immune system.
What Is Herpes Zoster Of The Eye
Herpes zoster, commonly known as “shingles,” is a viral disease that causes a painful skin rash consisting of small fluid-filled blisters that form scabs and can leave permanent scars. When it involves the region that surrounds your eye, it is called herpes zoster ophthalmicus and can cause serious eye problems including corneal ulcers, inflammation, and glaucoma.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Test For Genital Herpes
Acute Retinal Necrosis And Progressive Outer Retinal Necrosis Syndromes
Herpes zoster virus is considered the offending agent in most cases of acute retinal necrosis and progressive outer retinal necrosis syndromes. Compared with acute retinal necrosis, progressive outer retinal necrosis is a more severe viral retinitis observed in immunocompromised persons, often in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Symptoms include blurred vision and/or pain in one or both eyes. Acute retinal necrosis is characterized by peripheral patches of retinal necrosis that rapidly coalesce , occlusive vasculitis, and vitreous inflammation. Conversely, immunocompromised patients with progressive outer retinal necrosis are unable to mount a vitreous inflammatory response, leading to rapid involvement of the macula. Both conditions commonly cause retinal detachment. The prognosis is extremely poor in patients with progressive outer retinal necrosis most patients have no light perception vision.14 The visual prognosis in patients with acute retinal necrosis is better, with many patients achieving a visual acuity of 20/40.15 Bilateral involvement in both forms is observed in one third of patients but may be as high as 70 percent in patients with untreated disease.16 Treatment includes long courses of oral and intravenous acyclovir , and corticosteroids.
The rightsholder did not grant rights to reproduce this item in electronic media. For the missing item, see the original print version of this publication.
FIGURE 5.
Live Attenuated Zoster Vaccine
The live attenuated zoster vaccine significantly boosts VZV-specific cellular immunity in older adults which provides the scientific rationale for using the vaccine because cellular immunity to VZV declines with age . The clinical rationale for the zoster vaccine lies in the facts that herpes zoster causes substantial morbidity, antiviral therapy does not prevent PHN and must be initiated within 72 hours of rash onset for maximum benefit, and PHN treatments are incompletely effective and often poorly tolerated by older adults.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the CDC recommends the live attenuated zoster vaccine for the prevention of herpes zoster and PHN in immuncompetent adults 60 years of age and older . Anaphylactic reactions to gelatin or neomycin with leukemia, lymphomas, or other malignant neoplasms affecting the bone marrow or lymphatic system on immunosuppressive therapy, including high-dose corticosteroids lasting two or more weeks with AIDS or other clinical manifestations of HIV, including persons with CD4+ T-lymphocyte values â¤200 per mm3 undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or receiving recombinant human immune mediators and immune modulators are contraindications to the live attenuated zoster vaccine. The live attenuated zoster vaccine can be given simultaneously with other inactivated vaccines including influenza, pneumococcal polysaccharide and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines .
You May Like: Can I Donate Blood If I Have Herpes
Is A Vaccine Available To Prevent Shingles
Two vaccines are available in the United States to reduce your chance of developing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. One vaccine, Zostavax®, has been available since 2006. The second vaccine, Shingrix®, has been available since 2017. Shingrix is recommended as the preferred vaccine by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of medical and public health experts.
Shingrix® is given as a two-dose shot in the upper arm. You should receive the second dose two to six months after receiving the first. Shingrix has been shown to be more than 90% effective in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. Its effectiveness remains above 85% for at least four years after receiving the vaccine.
Due to high levels of demand for the Shingrix vaccine and a supply shortage, the vaccine manufacturer is managing the timing and distribution of the vaccine throughout the United States. It plans to continue to manage the availability of the vaccine and hopes to make available the same or increased number of doses and to shorten the wait time for delivery this year .
How Do You Treat Herpes Rash
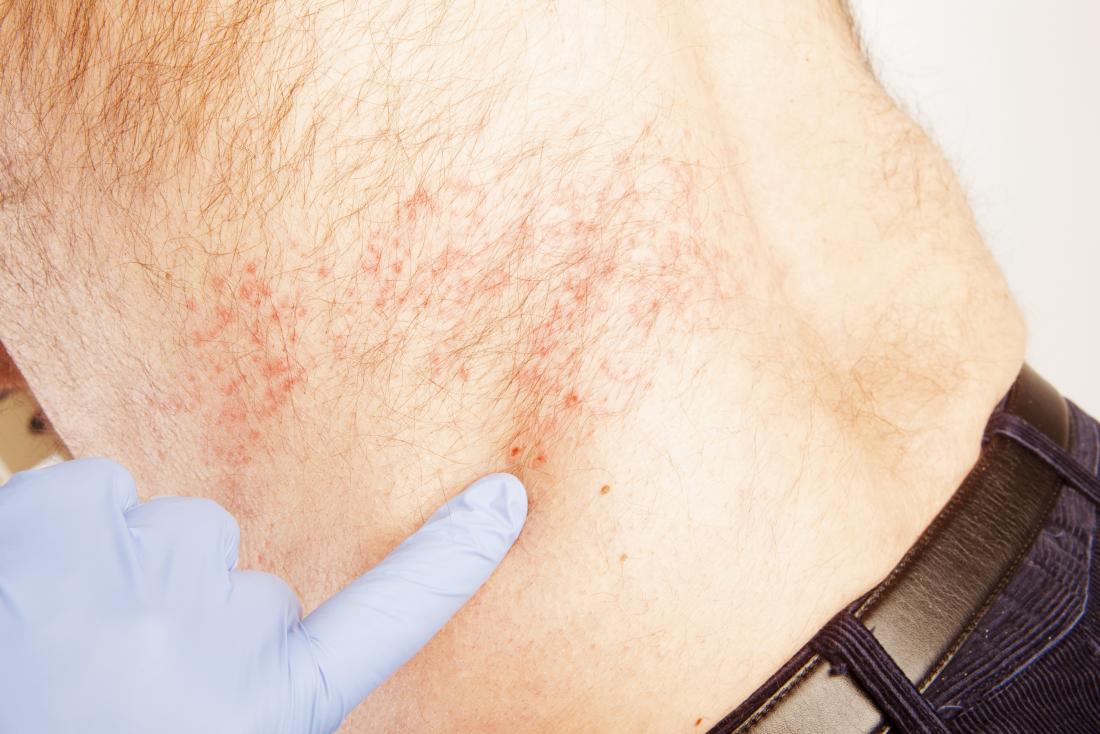
How do you treat herpes rash If you had severe pain during the active rash or have impaired senses, you are at increased risk for PHN. The elderly are also at greater risk. Early treatment of shingles may prevent PHN. Pain relievers and steroid treatment may be used to treat the pain and inflammation.
Also Check: How To Remove Herpes Bumps
Why Does Shingles Appear Mostly On One Side Or In One Area Of The Body
The virus travels in specific nerves, so you will often see shingles occur in a band on one side of the body. This band corresponds to the area where the nerve transmits signals. The shingles rash stays somewhat localized to an area it does not spread over your whole body. The torso is a common area, as is the face.
Cold Sore On Side Of Mouth
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and several cancer medications can cause mouth sores, ulcers, and tender gums. All can cause your mouth, throat, and tongue to feel sore, raw, or dry and may lead to dehydration, poor eating, and weight loss. The following tips and recommendations may help you to better manage your sore mouth, throat, and tongue.
Read Also: What Genital Herpes Feels Like
Why Doesnt Having Chickenpox Earlier In Life Provide Immunity Against Having Shingles Later
After having chickenpox, your body does not rid your system of the virus. Instead, the virus stays in a portion of the spinal nerve root called the dorsal root ganglion. In most people, the virus simply stays there quietly and doesnt cause problems. Scientists arent always sure why the virus gets active again, but they know stress can be a cause.
Is Shingles Prevention Possible Is There A Shingles Vaccine
Prevention of shingles in people who have contracted chickenpox is difficult, since the factors that trigger reactivation are not yet defined. However, if a person is never infected with the virus, shingles will not develop. Furthermore, there are at least two methods that are currently used to reduce the incidence of shingles.
First, the VZV vaccine, otherwise known as the chickenpox vaccine, may decrease the incidence of shingles by enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight off VZV or keep this virus inactive. This vaccine is usually administered to children, but the immunity may decline in about 15-20 years. The single-dose vaccine dose is given to babies 12-18 months of age. Most vaccine side effects, if they occur, are mild and range from a rash, skin redness, and swelling to small chickenpox lesions, usually at the injection site. Boosters of this vaccine for use in adults are now being investigated and may help prevent shingles in the future.
Shingrix is the vaccine the CDC currently recommends as the preferred shingles vaccine. Two doses about 2-6 months apart are more than 90% effective in preventing shingles and PHN, and it is recommended for use in people 50 and over. Side effects of Shingrix may occur and last about 2-3 days and may include redness and swelling at the inoculation site. Some individuals may experience muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, and nausea.
Recommended Reading: What To Do For Herpes Outbreak
Are There Any Herpes Vaccines Currently Being Studied
Yes, vaccines are currently being researched to target both HSV-1 and HSV-2. Most of these vaccines are being developed for HSV-2 since it can cause more dangerous infections. But since the viruses are so similar, an HSV-2 vaccine would also likely work to prevent or treat HSV-1, too.
You may be wondering if vaccines being researched will help people who are already infected, in addition to those who havent been exposed to the virus. Luckily, studies are underway on both treatment and preventative vaccines. More on these vaccine types next.
Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus is a serious, vision-threatening infection that affects the eye and the skin surrounding the eye. HZO is caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox in children. After infection, the virus remains dormant in the nerves and can reactivate, resulting in shingles in people with weakened immune systems. HZO is caused when the virus is reactivated in the nerves that supply the eye area.
The varicella-zoster virus is not to be confused with herpes simplex 1, another virus that causes eye herpes. Herpes simplex 1 is the same virus that causes cold sores on the lips and mouth. It sometimes causes an infection of the cornea called herpes simplex keratitis.
Don’t Miss: What Is Anti Herpes Medication