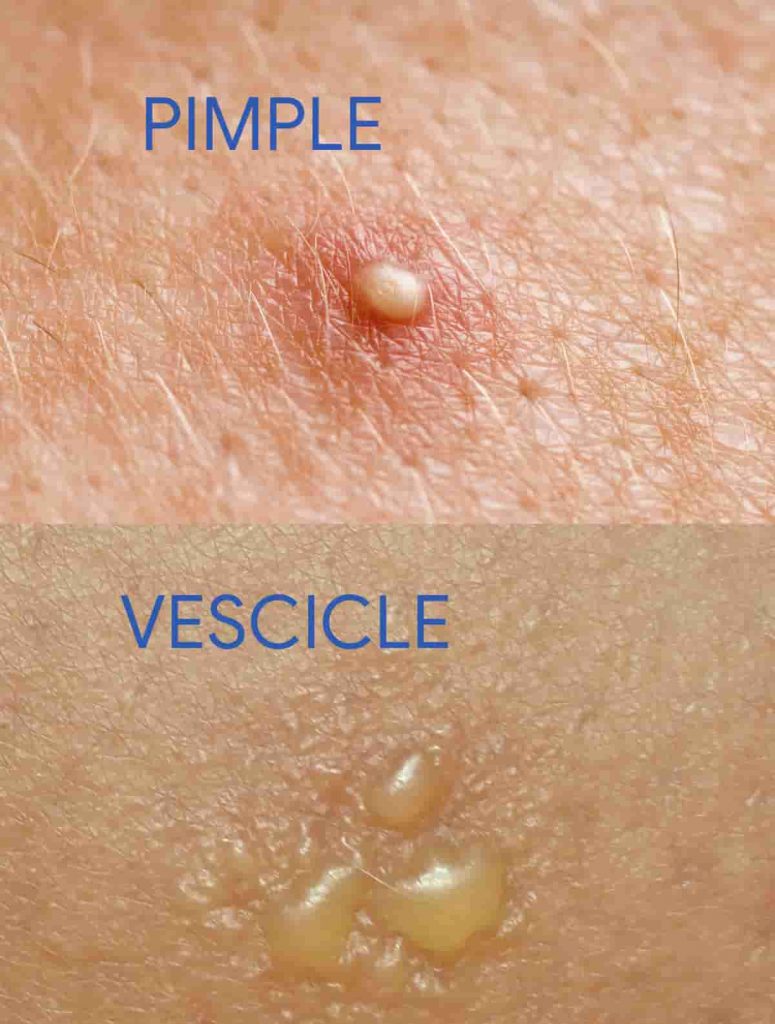
The Seven Strains Of Herpes
- Copy article link
Dear Dr. Reinisch: What other kinds of herpes are there besides genital herpes? A member of my family occasionally has a herpes sore on her thigh. She has never mentioned having it in the genital area.
Dear Reader: Seven different kinds of herpes virus have been identified in humans: varicella-zoster virus , Epstein-Barr Virus , cytomegalovirus , human herpesvirus 6 , human herpesvirus 7 , herpes simplex virus-1 and herpes simplex virus-2 .
Varicella-zoster virus causes chicken pox and shingles. Epstein-Barr virus causes infectious mononucleosis. Cytomegalovirus is often seen in those with immune system disorders and results in a number of conditions. HHV-6 is responsible for roseola in infants and young children. And HHV-7 has been identified in the laboratory, but it is not known whether it causes disease.
In this column, I most often answer questions about the herpes simplex viruses. HSV-1 is commonly found around the mouth in the form of cold sores or fever blisters. HSV-2 most often causes sores in the genital area. However, it isn’t unusual for HSV-2 to be around the mouth or HSV-1 to be at genital sites.
Whats The Difference Between Oral And Genital Herpes
Its an oversimplification to say that HSV-1 causes oral herpes and HSV-2 causes genital herpes, though these are the easiest definitions of each.
HSV-1 is a subtype of the herpes virus that typically causes oral herpes. This is also known as cold sores.
HSV-1 can also cause genital blisters that appear very similar to the genital blisters associated with HSV-2 virus.
Any herpes sore or blister regardless of its subtype can burn, itch, or tingle.
The HSV-2 subtype of the herpes virus causes genital sores, as well as swollen lymph nodes, body aches, and fever.
Although HSV-2 can also cause sores on the face, its much less common than genital sores.
Its difficult to look at a herpes sore and determine whether it was caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2.
To make a diagnosis, a doctor or other healthcare provider would have to take a sample of fluid from a blister lesion or take a small sample of the skin lesion and send it to a lab for testing.
Theres also a blood test available.
How Can Herpes Be Prevented
Correct and consistent use of latex condoms can reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of transmitting or acquiring genital herpes because herpes virus shedding can occur in areas that are not covered by a condom.25,26
The surest way to avoid transmission of STDs, including genital herpes, is to abstain from sexual contact, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested for STDs and is known to be uninfected.
Persons with herpes should abstain from sexual activity with partners when herpes lesions or other symptoms of herpes are present. It is important to know that even if a person does not have any symptoms, he or she can still infect sex partners. Sex partners of infected persons should be advised that they may become infected and they should use condoms to reduce the risk. Sex partners can seek testing to determine if they are infected with HSV.
Daily treatment with valacyclovir decreases the rate of HSV-2 transmission in discordant, heterosexual couples in which the source partner has a history of genital HSV-2 infection. 27 Such couples should be encouraged to consider suppressive antiviral therapy as part of a strategy to prevent transmission, in addition to consistent condom use and avoidance of sexual activity during recurrences.
Don’t Miss: Can Abreva Be Used On Genital Herpes
Herpes Simplex Cns Infection
-
Polymerase chain reaction of cerebrospinal fluid and MRI for HSV encephalitis
Diagnosis of HSV infection is often clinical based on characteristic lesions.
Laboratory confirmation can be helpful, especially if infection is severe, the patient is immunocompromised or pregnant, or lesions are atypical. A Tzanck test often reveals multinucleate giant cells in HSV or varicella-zoster virus infection.
Definitive diagnosis is with culture, seroconversion involving the appropriate serotype , PCR, and antigen detection. Fluid and material for culture should be obtained from the base of a vesicle or of a freshly ulcerated lesion. HSV can sometimes be identified using direct immunofluorescence assay of scrapings of lesions. PCR of CSF and MRI are used to diagnose HSV encephalitis.
HSV should be distinguished from herpes zoster Herpes Zoster Herpes zoster is infection that results when varicella-zoster virus reactivates from its latent state in a posterior dorsal root ganglion. Symptoms usually begin with pain along the affected… read more , which rarely recurs and usually causes more severe pain and larger groups of lesions that are distributed along a dermatome and typically do not cross the midline.
Clusters of vesicles or ulcers on an erythematous base are unusual in genital ulcers other than those due to HSV infection.
How Is Genital Herpes Diagnosed
HSV nucleic acid amplification tests are the most sensitive and highly specific tests available for diagnosing herpes. However, in some settings viral culture is the only test available. The sensitivity of viral culture can be low, especially among people who have recurrent or healing lesions. Because viral shedding is intermittent, it is possible for someone to have a genital herpes infection even though it was not detected by NAAT or culture. 11
Type-specific virologic tests can be used for diagnosing genital herpes when a person has recurrent symptoms or lesion without a confirmatory NAAT, culture result, or has a partner with genital herpes. Both virologic tests and type-specific serologic tests should be available in clinical settings serving patients with, or at risk for, sexually transmitted infections. 11
Given performance limitations with commercially available type-specific serologic tests , a confirmatory test with a second method should be performed before test interpretation. If confirmatory tests are unavailable, patients should be counseled about the limitations of available testing before serologic testing. Healthcare providers should also be aware that false-positive results occur. In instances of suspected recent acquisition, serologic testing within 12 weeks after acquisition may be associated with false negative test results. 11
Providers are strongly encouraged to look at CDCs STI Treatment Guidelines for further diagnostic considerations.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Herpes Outbreak Getting Worse
Herpes And Newborn Infants
Herpes infection in a newborn can cause a range of symptoms, including skin rash, fevers, mouth sores, and eye infections. If left untreated, neonatal herpes is a very serious and even life-threatening condition. Neonatal herpes can spread to the brain and central nervous system, causing encephalitis and meningitis. It also can lead to intellectual disability, cerebral palsy, and death. Herpes can also spread to internal organs, such as the liver and lungs.
Infants infected with herpes are treated with acyclovir, an antiviral drug. They usually receive several weeks of intravenous acyclovir treatment, often followed by several months of oral acyclovir. It is important to treat babies quickly, before the infection spreads to the brain and other organs.
Suppressive Therapy For Recurrences
To suppress outbreaks, treatment requires taking pills daily on a long-term basis. Acyclovir and famciclovir are taken twice a day for suppression. Valacyclovir is taken once a day. The doses for these antiviral drugs are reduced in people with impaired renal function.
Suppressive treatment can reduce the frequency of outbreak recurrences by 70% to 80%. It is generally recommended for people who have frequent recurrences . Because herpes recurrences often diminish over time, you should discuss annually with your provider whether you should stay with drug therapy or discontinue it.
There is some evidence that valacyclovir may help prevent herpes transmission, particularly in situations where one heterosexual partner has HSV-2 and the other partner does not. However, this drug does not completely prevent transmission. While taking any suppressive therapy for genital herpes, it is still important to regularly use latex condoms and to avoid any sexual activity during recurrences.
Recommended Reading: Can Herpes Cause Kidney Infection
How Do I Know If I Have Hpv
There is no test to find out a persons HPV status. Also, there is no approved HPV test to find HPV in the mouth or throat.
There are HPV tests that can screen for cervical cancer. Healthcare providers only use these tests for screening women aged 30 years and older. HPV tests are not recommended to screen men, adolescents, or women under the age of 30 years.
Most people with HPV do not know they have the infection. They never develop symptoms or health problems from it. Some people find out they have HPV when they get genital warts. Women may find out they have HPV when they get an abnormal Pap test result . Others may only find out once theyve developed more serious problems from HPV, such as cancers.
How Can I Avoid Hpv And The Health Problems It Can Cause
You can do several things to lower your chances of getting HPV.
Get vaccinated. The HPV vaccine is safe and effective. It can protect against diseases caused by HPV when given in the recommended age groups.
Get screened for cervical cancer. Routine screening for women aged 21 to 65 years old can prevent cervical cancer.
If you are sexually active:
- Use condoms the right way every time you have sex. This can lower your chances of getting HPV. But HPV can infect areas the condom does not cover. So, condoms may not fully protect against getting HPV and
- Be in a mutually monogamous relationship or have sex only with someone who only has sex with you.
You May Like: Herpes Simplex 2 Symptoms Male
So Cold Sores Are Only Caused By Hsv
Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can cause cold sores on the mouth and face.
Although its more common for HSV-1 to cause cold sores, it isnt impossible for HSV-2 to cause them, too.
Cold sores arent the same thing as canker sores or mouth ulcers. They each have different causes and two entirely different presentations.
Cold sores:
- are caused by the herpes simplex virus
- usually develop near the outside of the mouth, such as below your nostrils or on your lips
- cause redness and fluid-filled blisters
- usually appear in groups
- eventually break and ooze, forming a crust-like scab
- may take 2 to 4 weeks to completely heal
Canker sores:
- may be caused by food or chemical sensitivities, dietary deficiencies, minor injury, or stress
- may develop anywhere inside your mouth, such as at the base of your gum line, inside your lip, or under your tongue
- are shaped like a circle or oval
- are typically yellow or white with a red border
- may appear solo or in groups
- usually take 1 to 2 weeks to completely heal
HSV-1 is spread through direct contact with the virus, which can be present in or around cold sores, in oral secretions , and in genital secretions .
Some of the ways it can be transmitted include:
- kissing someone on the mouth
- sharing eating utensils or cups
- sharing lip balm
- performing oral sex
The herpes virus usually affects the area where it first made contact with the body.
Some of the ways HSV-2 can be transmitted include:
Myth #: Herpes Is Not Harmful
Fact: Most of the time, herpes is mild. However, it can cause serious complications in some cases.
For example, having HSV-2 can make a person three times more likely to contract HIV.
Also, if an infant has exposure to herpes during delivery, they are at risk of neonatal herpes. This can cause brain damage or death. Research suggests that neonatal herpes affects
Both types of herpes are most contagious when a person has symptoms. However, herpes can still spread when no symptoms are present.
Genital herpes spreads through sexual contact. The likelihood of a person spreading it will depend on:
- how often they have sex with another person
- if and how often they use barrier method contraception
- how long they have had herpes
Using barrier method contraception reduces the risk of spreading herpes to a sexual partner, but it cannot prevent it completely. Dental dams can reduce the risk of spread during oral sex, as herpes can pass between a persons mouth and their partners genitals.
Research shows that older herpes infections are less contagious than newer ones. In other words, if a person has had the virus for many years, they may be less likely to spread it than someone who has recently contracted it.
People can also get oral herpes through nonsexual contact with a person who has the virus. This contact may include kissing or sharing utensils or drinks.
Read Also: How Long Genital Herpes Outbreak Last
Myth #: People Cannot Spread Herpes To Others Unless They Have Sores Or Blisters
Fact: People can spread herpes to others at any time, including when they do not have any symptoms.
People with herpes may experience outbreaks and remissions. During an outbreak, a person has active sores or blisters, but in remission, they may have no symptoms at all.
The virus is usually more contagious when a person has an outbreak, but it can also spread when it is in remission.
Is Genital Herpes Related To Shingles
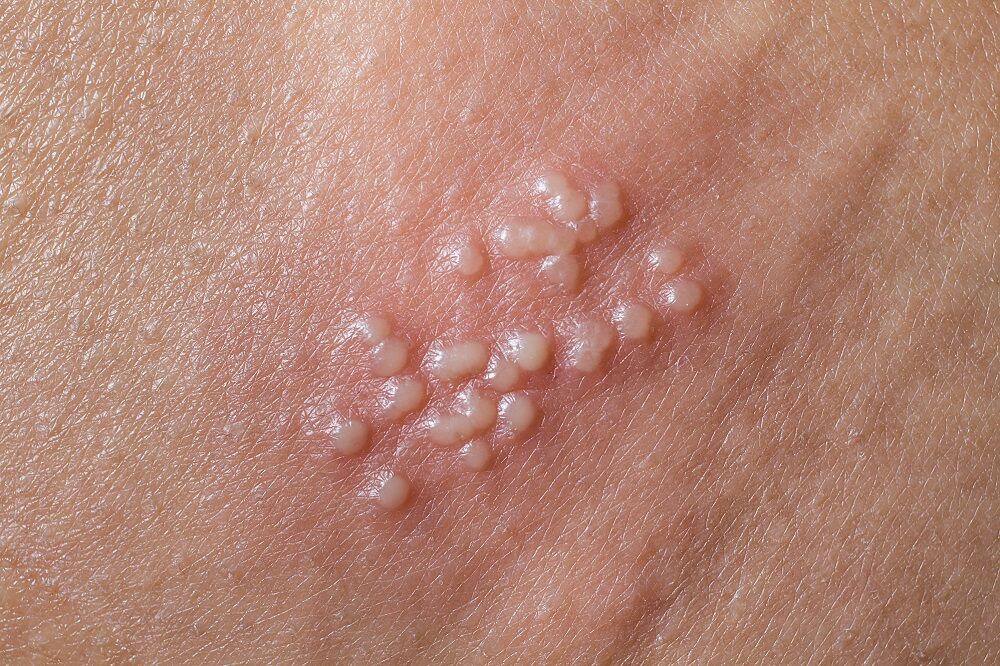
Shingles, also called herpes zoster, is caused by the varicella zoster virus , which causes chickenpox earlier in life. The natural history of varicella zoster infection is similar to genital herpes infection in that VZV also becomes latent in the sensory nerve roots. Later in life the virus may exit, causing shingles.
Recurrences in shingles cause blister lesions in a single area of skin called a dermatome. Shingles is not a sexually transmitted infection and is independent from genital herpes.
You May Like: How Long Do Herpes Outbreaks Last Without Medication
Is There Any Resistance To Genital Herpes Medication
Resistance to drugs that treat genital herpes even after 20 years of use is very rare. Herpes medications may not work as well in patients who are very immunosuppressed and have been treated with these drugs for a long time. Each individuals response to treatment may vary. In some cases, patients may need more drugs to suppress their viral outbreaks than others.
How Common Is Hpv And Health Problems That Develop From Hpv
HPV : CDC estimates that there were 43 million HPV infections in 2018. In that same year, there were 13 million new infections. HPV is so common that almost every sexually active person will get HPV at some point if they dont get vaccinated.
Health problems related to HPV include genital warts and cervical cancer.
Genital warts: Prior to HPV vaccines, genital warts caused by HPV affected roughly 340,000 to 360,000 people yearly.* About one in 100 sexually active adults in the U.S. has genital warts at any given time.
Cervical cancer: Every year, nearly 12,000 women living in the U.S. will have cervical cancer. More than 4,000 women die from cervical cancereven with screening and treatment.
There are other conditions and cancers caused by HPV that occur in people living in the United States. Every year, about 19,400 women and 12,100 men experience cancers caused by HPV.
*These figures only look at the number of people who sought care for genital warts. This could be less than the actual number of people who get genital warts.
You May Like: Can Genital Herpes Appear On Your Mouth
Myth #: People With Herpes Know That They Have It
Fact: Most people who have oral or genital herpes do not have any symptoms, according to the WHO .
Therefore, a person may not know that they have herpes, which means that they could unintentionally spread it to others.
The WHO state that only of people who have HSV-2 report receiving a diagnosis of genital herpes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Genital Herpes
Most individuals infected with HSV are asymptomatic or have very mild symptoms that go unnoticed or are mistaken for another skin condition. 9 When symptoms do occur, herpes lesions typically appear as one or more vesicles, or small blisters, on or around the genitals, rectum or mouth. The average incubation period for an initial herpes infection is 4 days after exposure. 10 The vesicles break and leave painful ulcers that may take two to four weeks to heal after the initial herpes infection. 5,10 Experiencing these symptoms is referred to as having a first herpes outbreak or episode.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent The Spread Of Genital Herpes
Human Herpesvirus Type 7
History
HHV-7 was discovered by Frenkel and colleagues69 in 1990 in a healthy person and was shown to be a cause of exanthem subitum.70
Description of the Virus
HHV-7, like HHV-6, is a member of the Roseolovirus genus and shares 20% to 75% amino acid identity with HHV-6 in many of their viral proteins.4 The HHV-7 genome contains about 145 kilobase pairs of DNA.
Epidemiology
HHV-7 infections occur at a later age than HHV-6 infections .6 About 18% of children are infected with HHV-7 by 1 year of age and 53% by 2 years. Most children are infected between ages 2 and 5 presumably from infected saliva of parents and siblings.71 HHV-7 DNA was detected in PBMCs from 67%, and in cervical swabs from 3%, of pregnant women.7 About 50% of HSCT and 20% of solid-organ transplant recipients reactivate HHV-7 as indicated by viral DNA in the peripheral blood.13,72
Pathogenesis
HHV-7 has a narrower tissue tropism than HHV-6. HHV-7 infects CD4+ T cells, epithelial cells in the salivary glands, and cells in the lungs and skin. HHV-7 is frequently shed in saliva at high levels throughout life in most adults and children.73 The virus has been detected in breast milk and establishes latency in CD4+ cells. HHV-7 induces degradation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules.
Clinical Manifestations
Laboratory Diagnosis
Therapy
Mary T. Caserta, in, 2018
What Are The Complications Of Genital Herpes
Genital herpes may cause painful genital ulcers that can be severe and persistent in persons with suppressed immune systems, such as HIV-infected persons. 5 Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can also cause rare but serious complications such as aseptic meningitis . 5 Development of extragenital lesions may occur during the course of infection. 5
There are also potential complications for a pregnant woman and her newborn child. See How does herpes infection affect a pregnant woman and her baby? below for information about this.
Recommended Reading: Do Herpes Outbreaks Happen In The Same Spot